Across-the-board Guide to Artificial Intelligence.
Featuring beginner-friendly examples and
serving as a reference book for professionals,
these ready-to-run simulations empower you to stand out from the crowd.
Introduction to symbolic AI
To be continued ...
Introduction to stateless vector AI
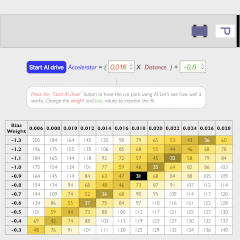 The simplest AI imaginable with just one neuron
The simplest AI imaginable with just one neuron
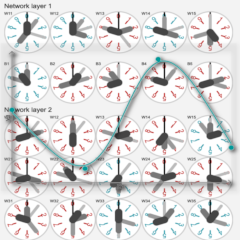 Curve fitting a workhorse of modern AI
Curve fitting a workhorse of modern AI
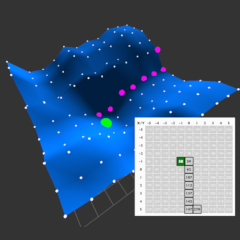 Gradient Decent vs. Simulated Annealing
Gradient Decent vs. Simulated Annealing
 The simplest AI imaginable with just one neuron
The simplest AI imaginable with just one neuron
Learn the basics of AI and experiment with a neural network consisting of a single neuron,
optimize parameters and experience how AI algorithms develop in real time.
Perfect for anyone who wants to understand the fundamentals of AI,
from aspiring data scientists, tech enthusiasts to average joe.
 Curve fitting a workhorse of modern AI
Curve fitting a workhorse of modern AI
Most people associate human-like machines that can see, speak and reason with brain-like neural
networks
that can think and reflect on a problem.
But Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) are mostly stateless and primarily master one thing: they
excel at
curve fitting, mapping input data to outputs through complex functions, enabling them to solve
diverse
problems, including training large language models (LLMs).
Let’s now demystify this core concept of modern AI
 Gradient Decent vs. Simulated Annealing
Gradient Decent vs. Simulated Annealing
This software demonstrates the solution to an optimization problem, using the example of the
shortest
route to a hospital. Optimization problems play a central role in machine learning.
To be continued ...
Stateful AI
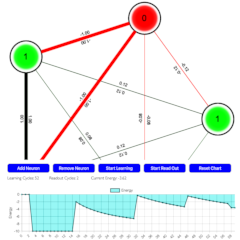 Hopfield / Boltzmann Network Simulation
Hopfield / Boltzmann Network Simulation
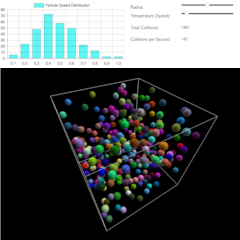 3D Gas Simulation
3D Gas Simulation
 Hopfield / Boltzmann Network Simulation
Hopfield / Boltzmann Network Simulation
The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to John J. Hopfield and Geoffrey Hinton for their
foundational work in artificial neural networks, which includes Hopfield networks and Boltzmann
machines. Their contributions have been instrumental in advancing machine learning and AI.
This simulation shows an energy-based neural network that is similar in function to Hopfield and
Boltzmann networks.
 3D Gas Simulation
3D Gas Simulation
The 3D gas simulation shows particles in a 3-dimensional space that meet and repel each other
depending
on the temperature. The energy distribution is shown as a diagram.
To be continued ...
Large Language Models
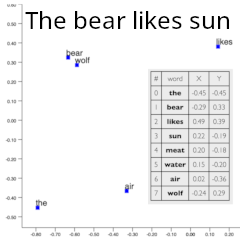 LLMs Part 1: Understand the meaning of words through AI
LLMs Part 1: Understand the meaning of words through AI
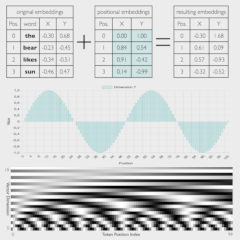 LLMs Part 2: Understand token position through AI
LLMs Part 2: Understand token position through AI
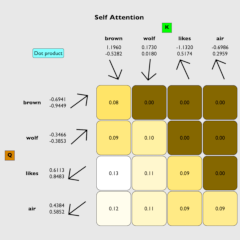 LLMs Part 3: Understand long context through AI
LLMs Part 3: Understand long context through AI
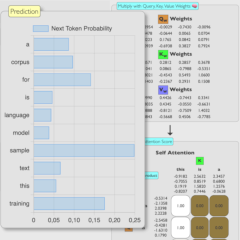 LLMs Part 4: Put the pieces together. The simplest LM imaginable
LLMs Part 4: Put the pieces together. The simplest LM imaginable
 LLMs Part 1: Understand the meaning of words through AI
LLMs Part 1: Understand the meaning of words through AI
This AI embedding algorithm
visualizes the relationships and meanings of words in a 2D vector space,
where every word tells a story through its position and connections.
This deep comprehension of word meanings forms the basic building block for large language models
(LLMs),
enabling them to generate coherent, contextually relevant text.
 LLMs Part 2: Understand token position through AI
LLMs Part 2: Understand token position through AI
Unlike traditional sequence models like Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), which process tokens
sequentially,
Transformers process all tokens in parallel and thus lack an inherent understanding of token order.
Positional encoding addresses this challenge by encoding positional information into the token
embeddings.
 LLMs Part 3: Understand long context through AI
LLMs Part 3: Understand long context through AI
The attention mechanism revolutionized NLP by enabling models to focus on important parts of the
input
sequence,
allowing for contextually accurate responses even in long sequences.
Introduced in the 2017 paper "Attention Is All You Need" by Vaswani et al., self-attention has
become a
cornerstone of
modern AI and the transformer architecture of LLMs.
 LLMs Part 4: Put the pieces together. The simplest LM imaginable
LLMs Part 4: Put the pieces together. The simplest LM imaginable
Let us now demystify the intricacies of Large Language Models (LLMs) and bring theory to life with
an interactive simulation.
Watch in real-time as this basic yet fascinating transformer model runs a live simulation,
piecing together language constructs with the elegance of simplicity.
To be continued ...
AI use cases
To be continued ...
Covered AI topics
Search AI systems excel at retrieving information quickly
and
efficiently, whether from
databases or the web.
NLP Understanding the meaning and context of language
and data is crucial for tasks like
natural language processing, enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Compression Reducing the size of data while preserving
important information is key for
efficient storage and transmission.
Planning AI can develop strategies and plan actions to
achieve
specific goals, particularly in
robotics and game playing.
Optimization AI algorithms often seek to find the best
solution to a problem, whether it's
minimizing costs or maximizing efficiency.
Approximation AI models approximate complex functions and
patterns in data, allowing for
predictions and decision-making.
Logical Reasoning AI can apply logical rules to draw
inferences and make decisions based on
available information.
Perception AI systems process sensory information, such as
visual, auditory, and tactile data,
to understand and interpret the world. This is crucial for tasks like image recognition and speech
processing.
Learning AI can adapt and improve from experience through
various learning methods, such as
supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. This capability is essential for tasks like
pattern
recognition and predictive analytics.
Interaction AI involves communication with humans or other
systems through natural language
processing, dialogue systems, and user interfaces. This is key for applications like virtual assistants
and
customer service bots.